The essential guide to image metadata
Image metadata is the invisible backbone of every photo, carrying the context, rights, and details that turn pictures into powerful, trustworthy assets.
When you open a photo, you’re only seeing part of its story. Beneath the surface lies a hidden layer of details known as image metadata, revealing the who, what, when, where, and how of its creation. This data turns a simple picture into an asset you can find, trust, and put to work in a digital world that never slows down.
From the precise GPS coordinates embedded in a smartphone snapshot to the crucial timestamp accompanying a press photograph, metadata on images quietly underpins our capacity to manage and, more importantly, trust visual content. Its evolution mirrors the journey of photography itself, moving from the handwritten notes on the backs of physical prints and the subtle watermarks on film negatives to the meticulously structured data automatically gathered by today's advanced devices.
Image metadata isn't just a technical curiosity; it's a critical component for businesses and individuals alike that use the power of images to craft compelling tales, market innovative products, treasure historical records, or deliver timely news. Image metadata ensures that every image is firmly anchored with the vital details needed to use it with confidence and accuracy, not just today, but for years to come.
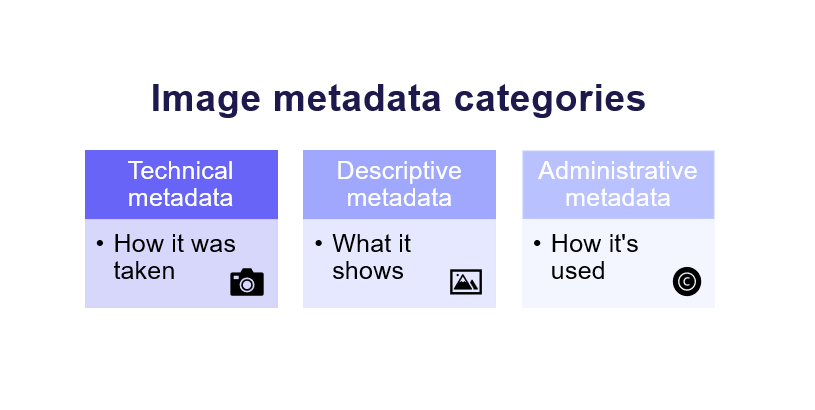
Breaking down image metadata types
If you want to understand why metadata in photos matters, you first need to know what image metadata actually is. You can think of it as a three-tier structure that follows an image from the moment you take it till the day you archive it.
- Technical metadata captures how the photo was taken. Your camera or phone automatically records details like shutter speed, aperture, ISO, resolution, and the device used. This information is invaluable for photographers, editors, and archivists who need to know the technical context behind every shot.
- Descriptive metadata explains what’s in the image and makes it searchable within a growing library. Captions, titles, keywords, alt text, and tags all fall into this category. Unlike technical metadata, these details often need a human touch to ensure they’re accurate and meaningful.
- Administrative metadata governs how an image can be used and who owns it. It includes copyright information, licensing terms, creator details, and any usage restrictions. For organizations, this metadata is essential for protecting intellectual property and staying compliant.
Devices capture important image metadata automatically, but in most professional workflows, that’s just a starting point. To truly organize, protect, and reuse your images at scale, you often need to enrich your images with more context, like rights info, project tags, and keywords — turning them from random files into structured, reliable assets you can find, share, and use with confidence.
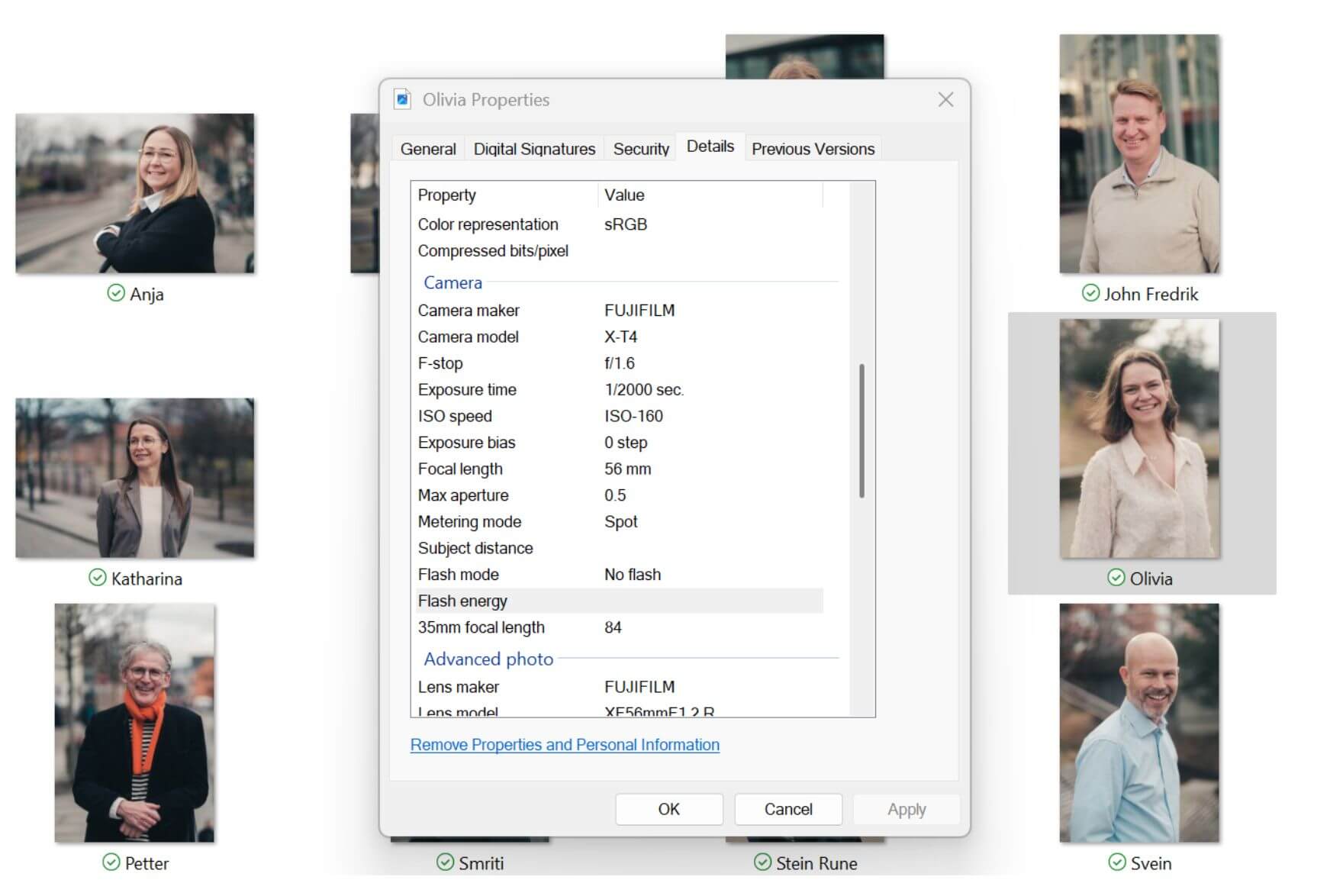
How to view image metadata - in Windows, MacOS - and at scale in advanced DAM systems

Why image metadata matters for professionals
When most people think about managing images, they think of folders, file names, and maybe some tagging in cloud storage. But image metadata is what actually makes an image readable, sortable, and searchable by both people and machines — even general-purpose tools like file explorers, Google Drive, or SharePoint use some metadata to deliver relevant results.
While these tools benefit from basic image metadata, more advanced and structured metadata through advanced metadata management opens up a whole new world of possibilities.
Image metadata values like creation date, file type, or resolution allow systems to sort and group images automatically.
Meanwhile, administrative metadata like copyright info and license terms help people understand how they can (and can’t) use the image, which reduces the risk of legal trouble.
And when photo metadata includes campaign names or expiration dates, automation engines can use that data to archive assets, route them for review, or expire them once they’re no longer valid.
What well-structured image metadata makes possible:
- Findability: Locate the right image fast, even without knowing the file name.
- Clarity: Know the who, what, when, and where right away.
- Protection: Clear rights and licensing details that prevent misuse.
- Structure: Group and organize assets automatically in a metadata-forward DAM.
- Verification: Confirm authenticity and track edits in an AI-saturated landscape.
- Automation: Trigger reviews, expirations, or distribution based on metadata fields.
Image metadata doesn’t just describe your images; it makes them functional.
From basic search to full-scale enterprise workflows, structured metadata helps every asset do its job.
Learn more: What is metadata management
Metadata plays a critical role in securing image authenticity
And in an age increasingly dominated by AI-generated visuals, image metadata's role in verifying image authenticity and tracking edits is becoming indispensable.
Organizations like the Content Authenticity Initiative (CAI) and C2PA are establishing standards to fully document an image's journey, bringing much-needed transparency and boosting trust in visual media.
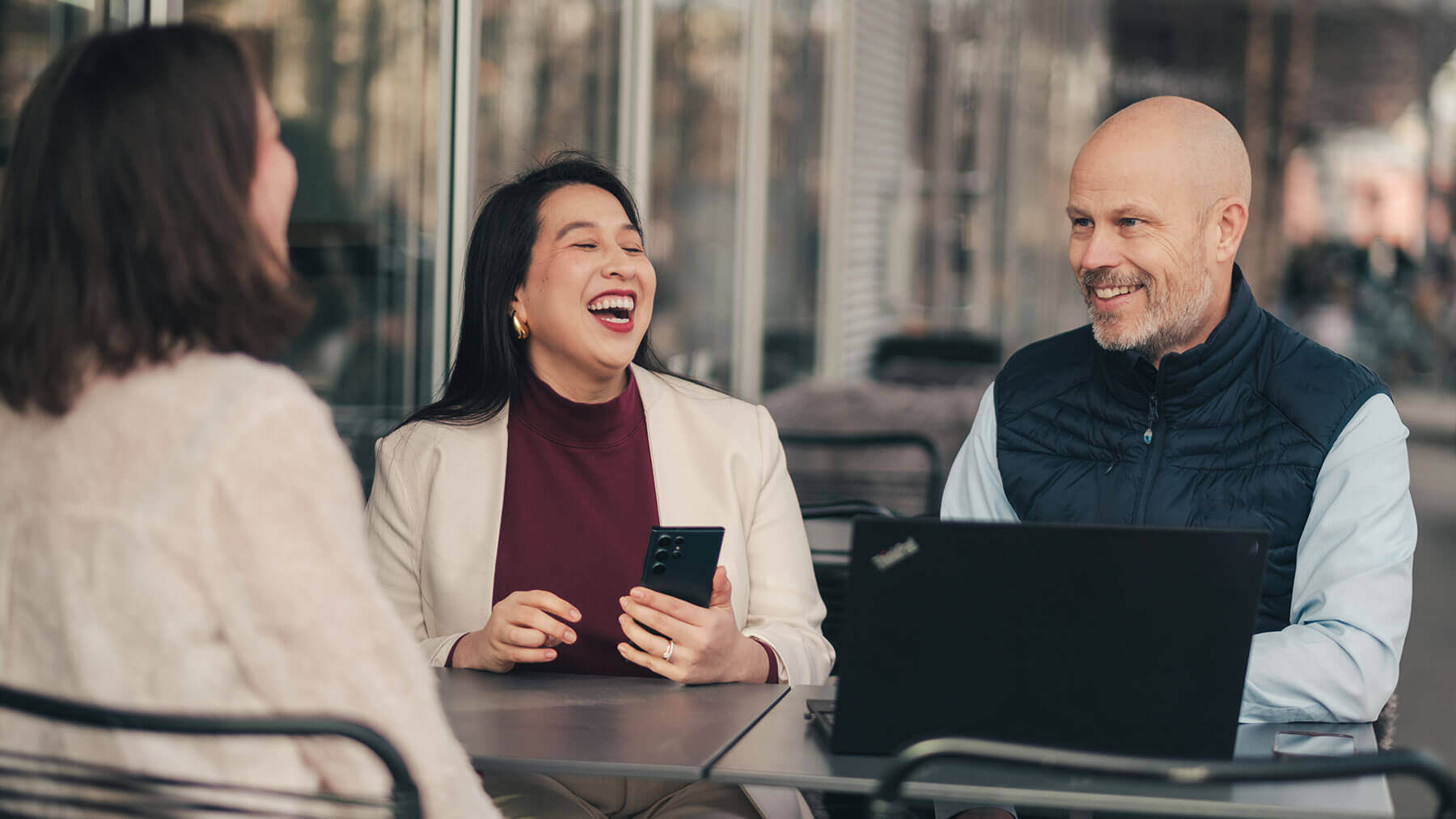

Metadata standards: the shared language of digital assets
Image metadata is especially valuable when it stays consistent and usable across all devices, systems, and workflows. This is exactly why metadata standards exist. They create a common language, letting different platforms easily understand, write, and exchange information.
By following standards, your image metadata remains structured, reliable, and readable across different tools and channels. Thereby increasing its reliability, while making it more likely to be interpreted as intended.
Here are the key standards that keep your image metadata intact:
- EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format)
Records technical information the moment a photo is taken, including shutter speed, ISO, and the capture date. This data provides insight into the conditions under which an image was created. - IPTC (International Press Telecommunications Council)
Commonly used in journalism and photography, IPTC metadata adds captions, credits, and rights information, maintaining context and ownership details as images are transferred between agencies, newsrooms, and archives. - XMP (Extensible Metadata Platform)
Developed by Adobe, enables the addition and management of information such as author names, licensing terms, and custom tags. It’s especially handy when working with large image libraries.
There are other standards too, including DCMI, PLUS, and VRA Core, which you’ll often find in libraries and archives. It’s normal for a single image to carry more than one image metadata standard, helping your files hold onto their details and context wherever they end up.
Understanding a photo’s metadata standards is one thing, but seeing how they work in practice is another.
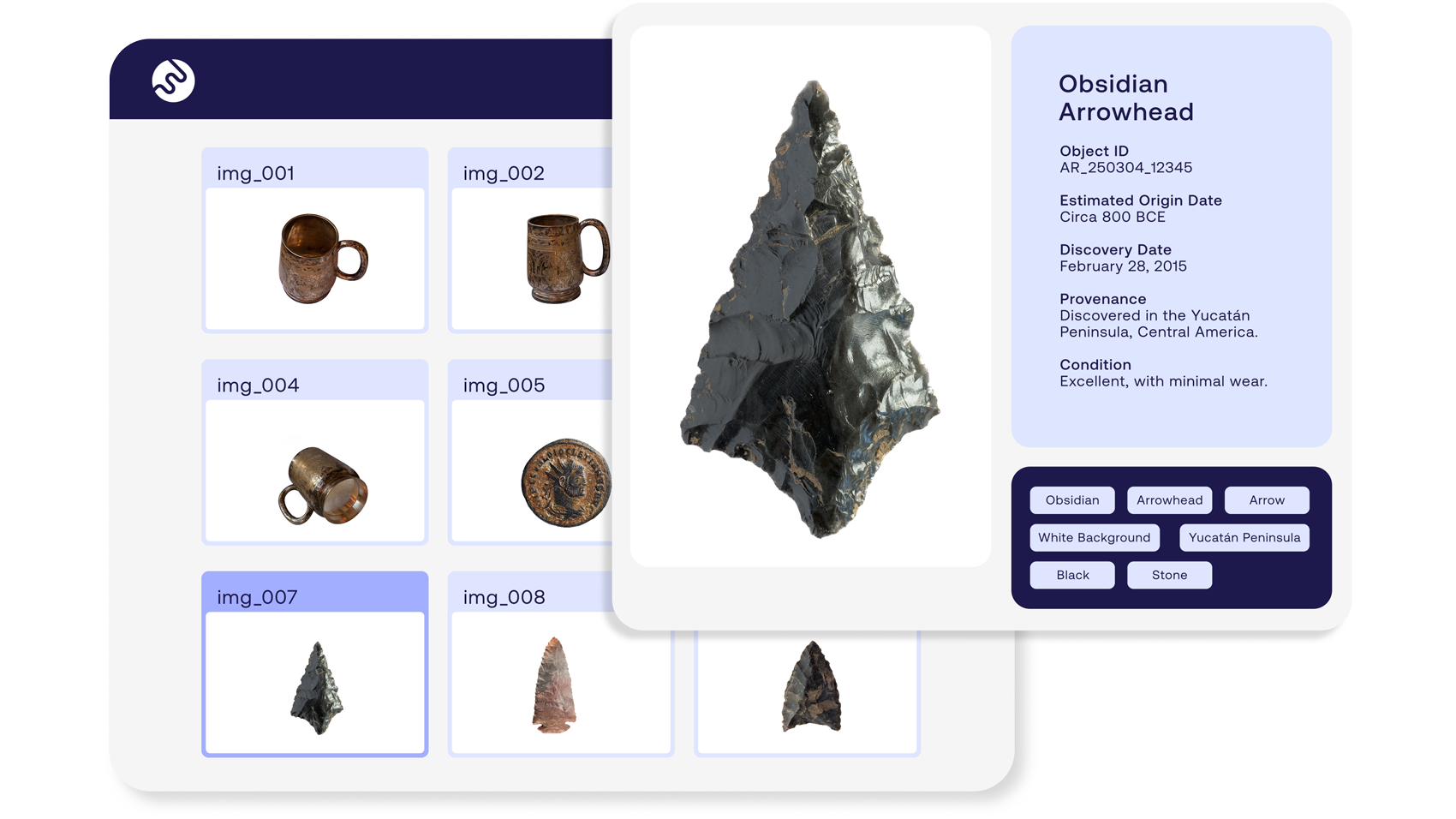
Metadata in action: How professionals use it daily
Image metadata's real purpose shows up daily in the hands of professionals who need to move fast, stay precise, and keep everything in control. It's what actually keeps image libraries functioning smoothly, protects your copyrights, and lets teams focus on their best work instead of constantly hunting for files or stressing about legal risks.
Here's how image metadata is a reliable asset across all kinds of industries:
- Photographers: It captures all the technical specifics of each shot, allowing them to learn from past projects, sharpen their skills, and ensure they get proper credit whenever their photos are shared or published.
- Museums & archives: Critical for preserving historical context and documenting where an item came from — making sure invaluable images remain discoverable, understandable, and trusted for generations.
- Marketing & communication: Makes it easy to find visuals by campaign, product, or region and stay in control of how they’re used. Embedded image metadata supports smarter scheduling, better performance tracking, and airtight rights compliance.
- Newsrooms: Makes sure that captions, bylines, and rights details stay connected to each image, allowing stories to go live without delays or legal issues.
- Law enforcement & digital forensics: Helps confirm whether an image is authentic and traces its path as evidence. Timestamps and location data provide the context needed to support investigations and courtroom use.

Drowning in image files?
When your image library grows, it’s easy to lose track of what you have and where to find it. Image metadata turns chaotic folders into organized libraries, enabling you to locate, trust, and use your visual assets without friction. A Digital Asset Management (DAM) system builds on the foundation of image metadata to help you maintain consistency, automate tagging, and keep your files secure and searchable across teams. Ready to bring order to your image library?
DAM: Where image metadata meets structure
Manual image metadata tagging might work when you're dealing with a small set of files, but as your library grows into the thousands, spread across teams, campaigns, and regions, consistency and usability start to break down.
Everyone needs to quickly find the right image and know it’s cleared, current, and approved for use. Without structure, that process gets slowed down and can introduce unnecessary risks.
A Digital Asset Management (DAM) system solves this by centralizing your visual assets and their image metadata. More advanced solutions, like Fotoware, go even further — reducing manual work through metadata-driven automations such as:
- Automatically adjusting access rights based on license dates or regional use.
- Adding contextual metadata when assets are tied to campaigns or publications.
Revoking or publishing assets based on usage criteria. - Maintaining a uniform metadata model for all linked content, teams, and tools.
This level of automation doesn’t just tidy up your library; it transforms how teams work with visual content across your entire organization.

How DAM systems use image metadata
Organizing your image library is one thing. Keeping images usable as your collection grows is another. A DAM system helps you do both. DAM solutions use image metadata to bring structure to your files while letting your team find and use images without the usual friction.
With a DAM, you can:
- Tag entire collections in one go, so you don’t lose time on repetitive tasks.
- Search for images using details like photographer, campaign, or licensing terms.
- Centralize your collection and give people (internally and externally) access to collaborate, review, and share content in one place.
- Control who sees what, defining exactly who can view, edit, or download each asset.
- Keep rights and licensing data connected to every file, so nothing slips through the cracks.
- Automate tasks like approvals, expirations, and archiving based on image metadata rules.
- Integrate with platforms you already use, with metadata guiding how and where content appears across systems.
Fotoware’s strengths lies in how flexibly it lets you work with metadata and on your terms. The platform supports everything from custom image metadata configurations and pre-ingestion workflows to integrations with external data sources, so you can shape processes that reflect how your organization actually works.
Whether it’s linking consent forms to specific assets, automating license-based access controls, or routing files based on campaign tags or usage rights, image metadata isn’t just something you add; it becomes part of how images move through your organization.
This level of structure helps teams stay aligned, reduces manual work, and ensures that every asset is context-rich, rights-cleared, and ready to use — without constant oversight.
Time to automate: Let image metadata do the work
Image metadata doesn’t just describe a file; it can drive what happens to it.
In advanced DAM systems, metadata in images becomes the engine behind powerful automations. Instead of relying on teams to tag, route, or restrict assets manually, the metadata embedded in each file can trigger actions based on rules you set.
For example:
- Automatically apply watermarks to images marked for external use
- Restrict access to files once their license expires
- Publish or revoke assets based on campaign metadata
- Add contextual tags (like location, channel, or product) the moment a file is uploaded.
- Automatically flag assets for review or archive them once they've served their purpose
- Mark image thumbnails based on usage status (e.g., draft, approved, expired).
These metadata-driven workflows reduce manual work, improve accuracy, and help organizations scale their content operations without losing control. It's how metadata transforms from a label to logic, which is encapsulated in each file.
Image metadata often goes unseen, but it quietly shapes how teams manage images, adding the details that give each photo its purpose.
It’s the difference between “I think we have that image somewhere” and “Here it is.”
When managed well, image metadata keeps projects moving, protects your brand, and helps people work with clarity and speed. It’s the layer that makes images ready for the moments that matter most.

What’s next?
Read our How to work faster with metadata-driven workflows
to learn how structured workflows can turn your images into assets.
or dive into our guide:





